Are you noticing changes in your body and suspecting that fibroids may be breaking down? Fibroids are relatively common among women, with up to 70-80% of white women and as many as 90% of African American women having experienced them at some point in their lives.
Although they usually don’t cause symptoms or require treatment, for those who experience the breakdown of fibroid tissue, it can lead to a range of signs and symptoms which, when left untreated, can have serious implications for overall health. In this blog post, we will provide an overview of what signs may indicate that fibroids are breaking down so you know what to look for.
What Is Fibroid Degeneration?
Fibroids are non-cancerous growths in the uterus. They comprise fibrous tissues and can range from very small to large, weighing several pounds. They usually don't cause symptoms or require treatment unless they start to break down (degenerate). This process is known as fibroid degeneration. When a fibroid begins to break down, it may cause a variety of signs and symptoms that can indicate a more serious underlying condition needing medical attention.
The exact cause of a fibroid breaking down is unknown, but some risk factors that may increase your chances include: being overweight, having high blood pressure, smoking cigarettes, taking oral contraceptives with estrogen or progesterone, and having had a previous injury to the uterus.
Types of Degenerating Fibroids
Necrosis
This is when a fibroid dies due to a lack of blood supply or other factors. Signs can include abdominal pain, fever, and vaginal discharge.
Cystic Degeneration
This is when the fibroids become filled with fluids and form cysts. Symptoms may include abdominal pain or swelling, urinary tract infections, and heavy menstrual bleeding.
Infection or Inflammation
A fibroid can become infected due to bacteria entering through a break in the tissue. Common signs of infection are fever, nausea, vomiting, bloody discharge from the vagina, and pelvic pain that worsens when touched.
Lipomatous Degeneration
Lipomatous degeneration is a type of fibroid degeneration where fat cells replace muscle tissue in the fibroid. This can lead to pain, discomfort, and inflammation.
Red Degeneration
This occurs when a fibroid experiences an interruption in its blood supply, leading to decreased oxygen and nutrients. The resulting discoloration or reddening of the fibroid may be accompanied by cramping and backache.
Calcific Degeneration
Fibroids that undergo calcific degeneration form calcium deposits in their structure leading to the hardening of the tissues and sometimes calcifying the uterus wall. Symptoms may include abdominal pain and tenderness, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
Hyaline Degeneration
This type of degeneration occurs when fibroids are deprived of oxygen and nutrients due to decreased blood flow or an interruption in their blood supply. This can lead to the formation of hyaline material, which is a clear jelly-like substance that can cause pelvic pressure or discomfort.
Hemorrhagic Degeneration
In this type of degeneration, fibroids become fragile and prone to bleeding or rupture due to low estrogen levels, leading to thinning of the uterine lining. This can cause heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding, and other symptoms may include abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and fever.
Fibroid Degeneration Symptoms
Abdominal Pain or Swelling
Abdominal pain, bloating, or swelling may be caused by a degenerating fibroid increasing in size due to fluid buildup.
Heavy Menstrual Bleeding
Heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding can indicate a dying fibroid and require medical attention.
Fever
A fever is the body’s natural response to an infection and can sometimes accompany a degenerative fibroid.
Nausea or Vomiting
Nausea and vomiting are common symptoms associated with fibroids breaking down.
Urinary Tract Infections
UTIs can occur along with a degenerative fibroid as bacteria from the vagina enter the uterus through breaks in tissue.
Pelvic Pressure or Discomfort
The degeneration of fibroids can lead to pressure or discomfort in the pelvic area.
Backache or Cramping
Backache and cramping are signs of a dying fibroid that require medical attention.
Bloody Discharge from Vagina:
Bloody discharge from the vagina can occur when a fibroid begins to break down due to infection.
Fatigue
Fatigue is often a symptom of a degenerative fibroid, as it requires increased energy for the body to combat the infection.
Fibroid Degeneration Causes
The exact cause of a fibroid breaking down is unknown, but some risk factors that may increase your chances include: being overweight, having high blood pressure, smoking cigarettes, taking oral contraceptives with estrogen or progesterone, and having had a previous injury to the uterus.
Additionally, underlying conditions like diabetes or endometriosis can increase the risk of degenerating fibroids. It’s also important to be aware that age can play a role in the risk of fibroids degenerating; older women are more likely to experience this process than younger women.
Fibroid Degeneration in Pregnancy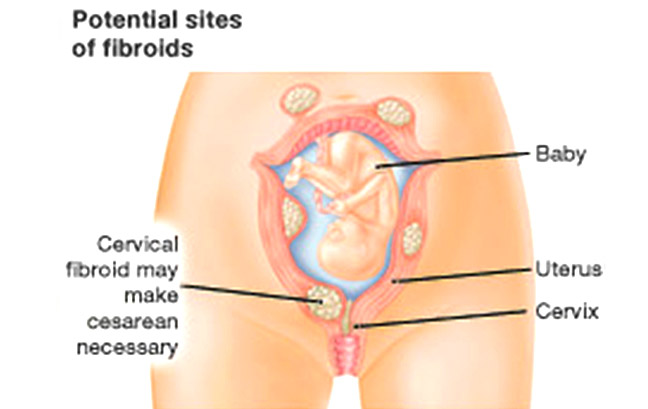
Fibroid degeneration in pregnancy is a medical condition that occurs when fibroids in the uterus break down and release toxins into the bloodstream. This can cause serious complications for both mother and baby, such as preterm labor, miscarriage, or even stillbirth.
The exact cause of fibroid degeneration during pregnancy is unknown, but it appears to be related to hormonal changes. As these hormones stimulate the growth of the uterus and its tissues, they may also affect the growth of any existing fibroids.
This can increase pressure on uterine walls, increasing the risk of fibroid breakdown. Additionally, some evidence suggests that certain medicines taken by pregnant women may increase their risk for this condition.
Fibroid Degeneration Diagnosis
Fibroid degeneration can be difficult to diagnose. It often presents with vague or no symptoms at all, so a doctor may need to perform several tests to determine if fibroids are the underlying cause.
The most common method of diagnosis is ultrasound imaging. This technique allows doctors to visualize the uterus and any existing fibroids and examine them for signs of degeneration. Additionally, MRI scans can provide detailed images that allow doctors to more precisely detect changes in tissue structure indicative of fibroid breakdown.
Blood tests can also aid in diagnosing this condition by detecting an abnormally high level of enzymes that indicate tissue death. Additionally, endometrial biopsy can help confirm the presence of degenerating fibroids.
FAQs
How do fibroids leave the body?
Fibroids can typically be expelled from the body naturally, through a process known as degeneration. During this process, the fibroid tissue gradually breaks down and is reabsorbed back into the body.
This occurs when the blood supply to the fibroid is decreased or cut off, causing it to die and slowly disappear. In some cases, however, medical intervention may be necessary if excessive bleeding or other symptoms need immediate treatment.
What does passing a fibroid look like?
Passing a fibroid typically looks like heavy menstrual bleeding or clots of tissue being expelled from the vagina.
This is because the uterine lining often becomes thinned out due to low estrogen levels, causing it to break apart and be released along with any other pieces of dead tissue that may have come loose during the process. You may also experience pain, cramping, nausea, fever, and fatigue as your body passes the fibroid.
Can fibroids cause infertility?
In some cases, if left untreated for too long, fibroids can lead to fertility problems due to their mass blocking off fallopian tubes or preventing fertilization from occurring successfully in the uterus.
In some cases, surgery may be needed to remove large fibroids that could cause infertility issues. Additionally, it’s important to remember that any uterine scarring or adhesions caused by fibroid degeneration can negatively impact fertility.
Conclusion
Fibroid degeneration is a relatively common process that can cause a range of signs and symptoms. While it typically doesn’t require medical intervention, it’s important to be aware of the warning signs so you can seek treatment if necessary. Additionally, understanding what fibroids are and how they can affect fertility is essential in ensuring optimal reproductive health. Consult your healthcare provider if you have any questions or concerns about fibroid breakdown.